ISO 9001:2015 Documentation Requirements
A Concentric Global White Paper by Jim Thompson & Sidney Porto
1 OPINION
Here at Concentric, we like change and typically embrace it. However, we are in agreement that several changes to the 2015 release of the ISO 9001 standard are just annoying. Changes that make understanding of the requirements less simple are, well… not simple. One example is the ambiguity associated with how many and what kinds of documented procedures and records are required. Now that the term "documented information" is being used, subscribers have to get out their ibuprofen, highlighters and dig down into the standard looking for clues like the words maintained (document required) and retained (record required). We've decided to create some more user-friendly tools to help you to better understand what's inside this 42-page document.
The following sections may be helpful in better understanding what is required vs. what is optional, for those of us who appreciate simple. All documented information, be it a traditional document or record, must be controlled in accordance with clause 7.5 Documented information. In order to make implementation and auditing simple, we recommend purchasing a printed copy of the standard and highlighting where the terms “maintained” and “retained” exist. The following sections can also be used as a quick reference guide to assist you in locating documentation requirements, examples of documents that may be used “as needed” and matrices to help you map standard references to your own language.
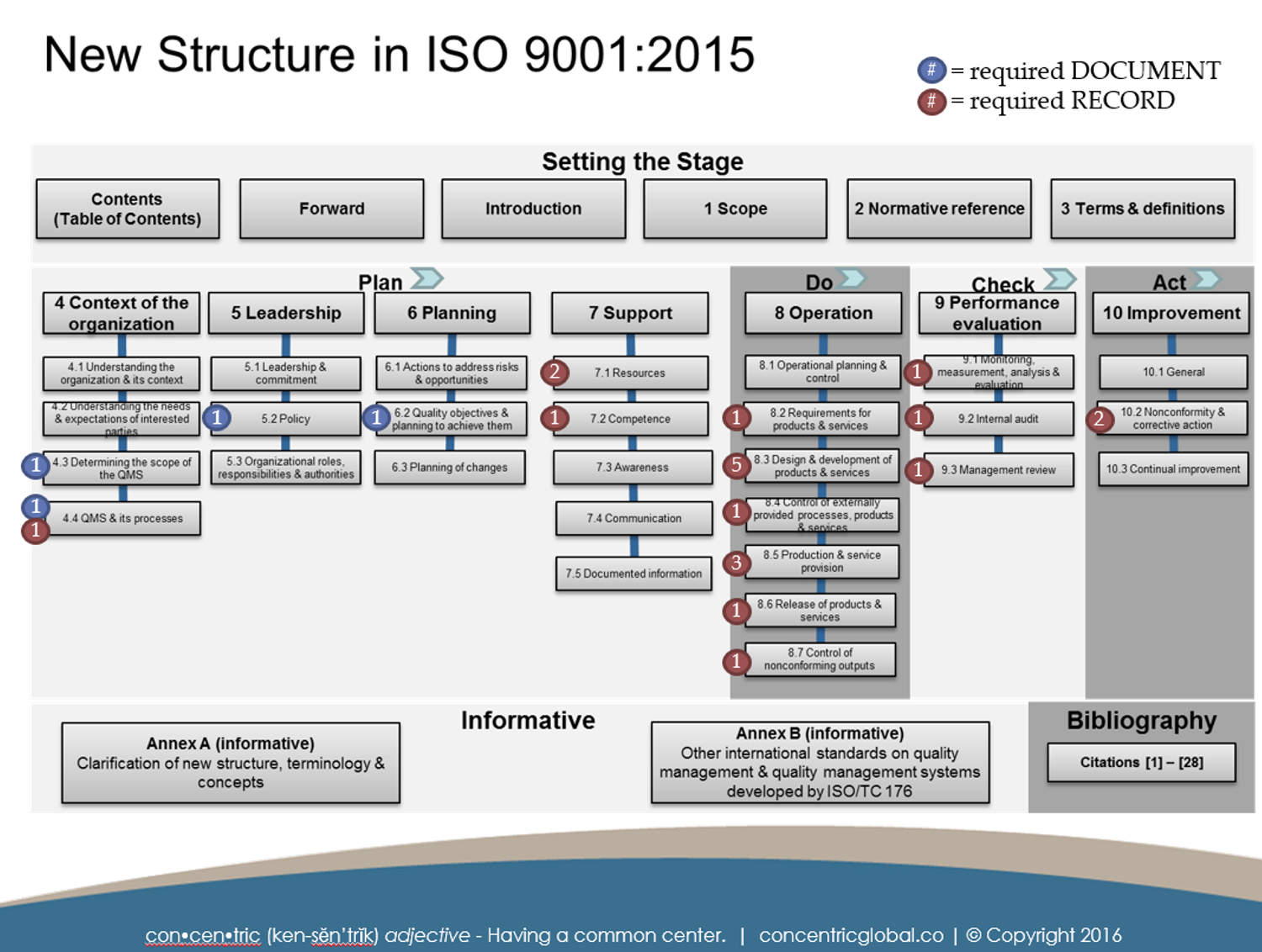
2 SUMMARY ILLUSTRATION OF REQUIRED DOCUMENTED INFORMATION
This illustration shows the requirements for maintaining and retaining documents based on the clause in which they appear. Blue circles indicate what is typically referred to as required document while the red circles indicate what is typically referred to as a record requirement.
3 REQUIRED DOCUMENTS
ISO 9001:2015 allows organizations more flexibility in the way it chooses which documents are necessary in order to achieve the results needed to meet and improve internal and customer requirements. ISO 9001 has always required a documented quality management system versus a system of documents for the sake of documented everything. In fact, often times we’ve seen organizations that have TOO MANY documents; making it very difficult for the key documents to be located. This breeds a risk for document users to rely on “tribal knowledge” rather than have faith in the documentation provided
The intent of an organization’s documented information is to communicate valuable information, provide evidence of conformities within required products/services and/or process performance, and for the exchange or retention of knowledge (referred to as “organizational knowledge”). Factors such as organizational size, type of activities/process/products/services, complexity/interaction of processes and competency of persons performing the work should be considered in determining what’s most suitable for an organization.
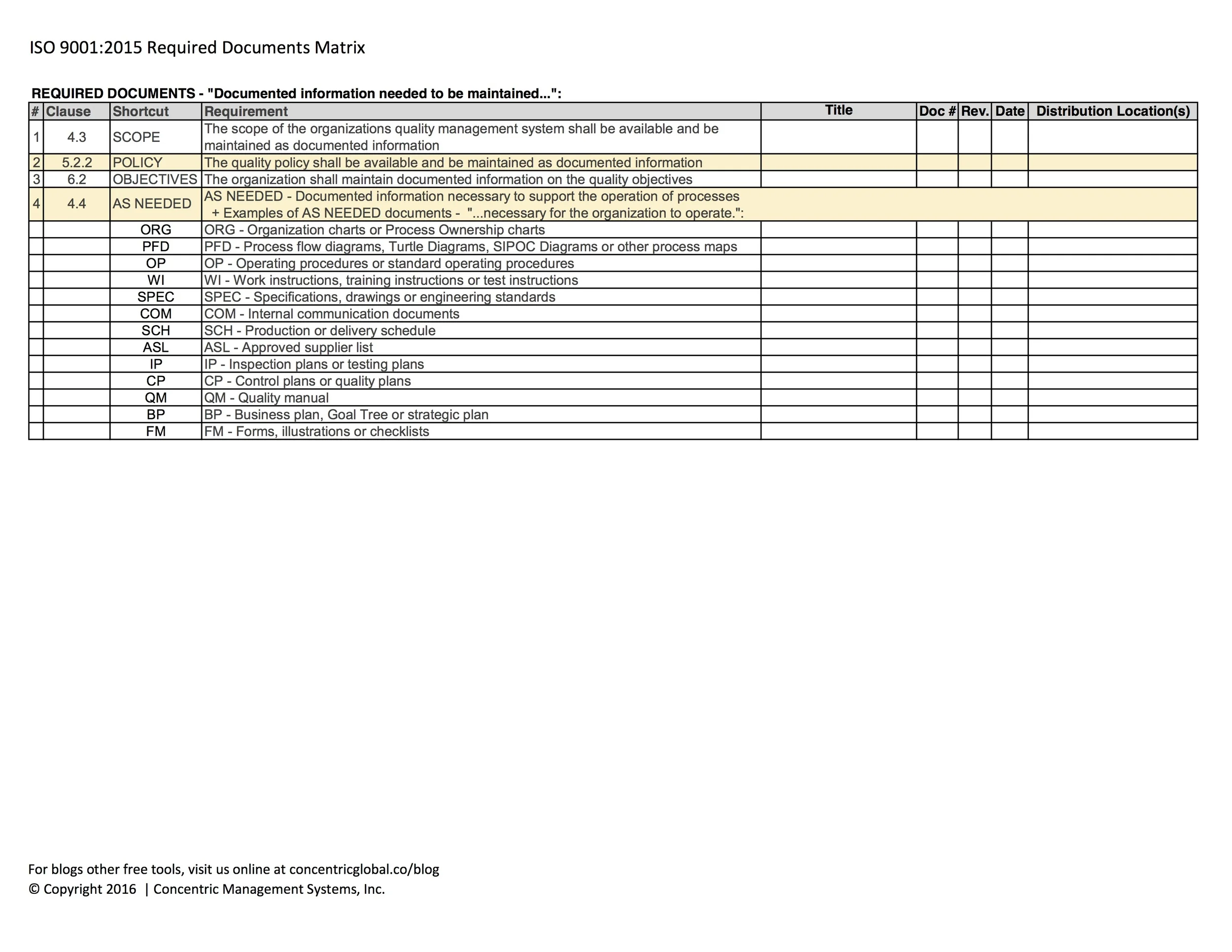
REQUIRED DOCUMENTS - "Documented information needed to be maintained...":
SCOPE - The scope of the quality management system (clause 4.3)
POLICY - The quality policy (clause 5.2.1)
OBJECTIVES - The quality objectives (clause 6.2)
AS NEEDED - Documented information necessary to support the operation of processes (clause 4.4)
+ Examples of AS NEEDED documents - "...necessary for the organization to operate.":
ORG - Organization charts or Process Ownership charts
PFD - Process flow diagrams, Turtle Diagrams, SIPOC Diagrams or other process maps
OP - Operating procedures or standard operating procedures
WI - Work instructions, training instructions or test instructions
SPEC - Specifications, drawings or engineering standards
COM - Internal communication documents
SCH - Production or delivery schedule
ASL - Approved supplier list
IP - Inspection plans or testing plans
CP - Control plans or quality plans
QM - Quality manual
BP - Business plan, Goal Tree or strategic plan
FM - Forms, illustrations or checklists
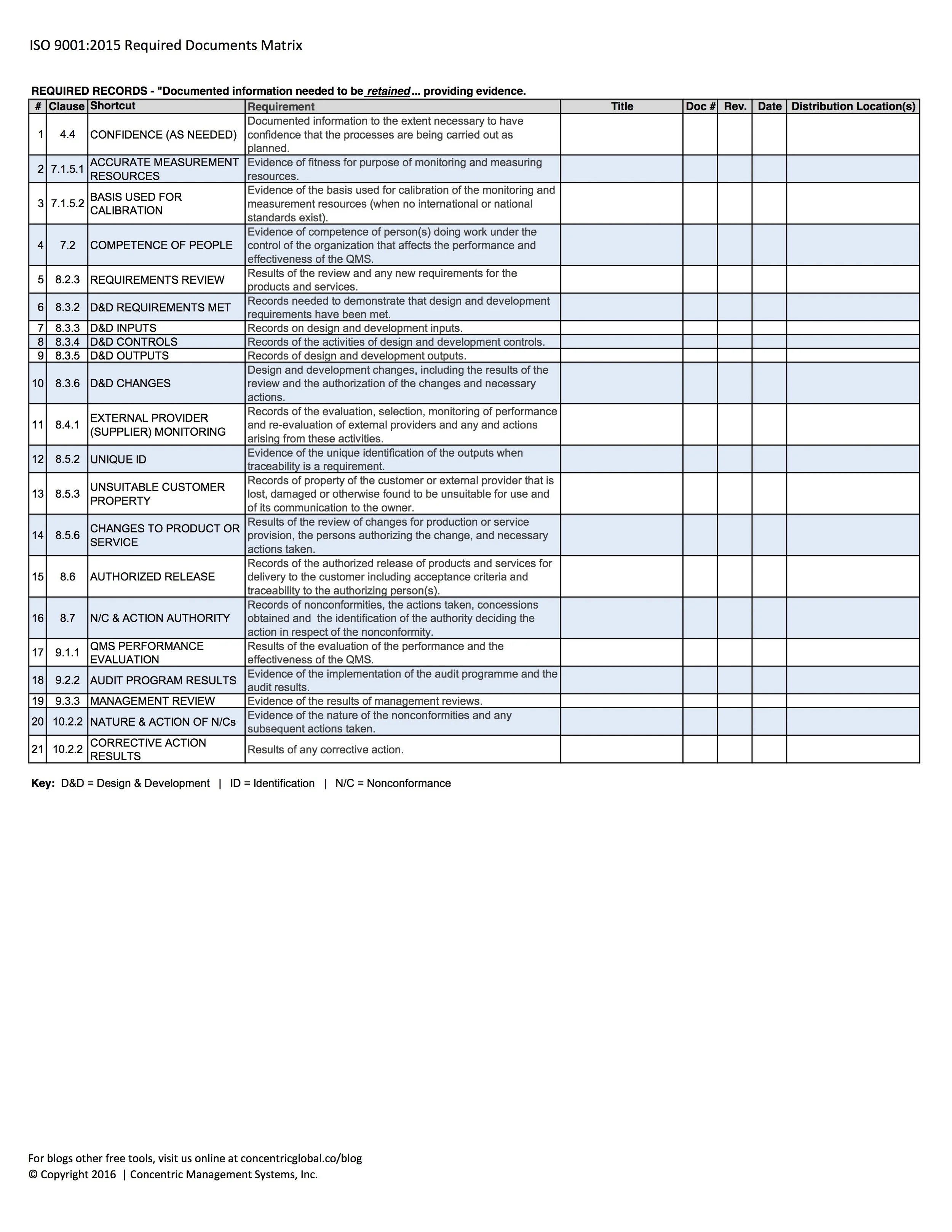
4 REQUIRED RECORDS
In the 2000 and 2008 versions of the standard, the reference to “(see 4.2.4)” was a simple flag that one could use to help identify when a record is required. This has been replaced by the term “retained”. The intent of retaining records is so that an organization can feel confident that operational inputs, process execution and process outputs are performing as intended. Records are often times use as documented evidence giving a person or machine the signal to proceed, stop or correct their course of action before moving forward.
Clauses for specific controls previously presented autonomously as 4.2.3 Control of documents and 4.2.4 Control of records have now been combined under 7.5.3 Control of documented information. The following 21 clauses represent minimum record requirements per the ISO 9001:2015 standard.
REQUIRED RECORDS - "Documented information needed to be retained... providing evidence.
CONFIDENCE (AS NEEDED) - "Documented information to the extent necessary to have confidence that the processes are being carried out as planned." (clause 4.4)
ACCURATE MEASUREMENT RESOURCES - Evidence of fitness for purpose of monitoring and measuring resources (clause 7.1.5.1).
BASIS USED FOR CALIBRATION - Evidence of the basis used for calibration of the monitoring and measurement resources (when no international or national standards exist) (clause 7.1.5.2).
COMPETENCE OF PEOPLE - Evidence of competence of person(s) doing work under the control of the organization that affects the performance and effectiveness of the QMS (clause 7.2).
REQUIREMENTS REVIEW - Results of the review and new requirements for the products and services (clause 8.2.3).
D&D REQUIREMENTS MET - Records needed to demonstrate that design and development requirements have been met (clause 8.3.2)
D&D INPUTS - Records on design and development inputs (clause 8.3.3).
D&D CONTROLS - Records of the activities of design and development controls (clause 8.3.4).
D&D OUTPUTS - Records of design and development outputs (clause 8.3.5).
D&D CHANGES - Design and development changes, including the results of the review and the authorization of the changes and necessary actions (clause 8.3.6).
EXTERNAL PROVIDER (SUPPLIER) MONITORING - Records of the evaluation, selection, monitoring of performance and re-evaluation of external providers and any and actions arising from these activities (clause 8.4.1)
UNIQUE ID - Evidence of the unique identification of the outputs when traceability is a requirement (clause 8.5.2).
UNSUITABLE CUSTOMER PROPERTY - Records of property of the customer or external provider that is lost, damaged or otherwise found to be unsuitable for use and of its communication to the owner (clause 8.5.3).
CHANGES TO PRODUCT OR SERVICE - Results of the review of changes for production or service provision, the persons authorizing the change, and necessary actions taken (clause 8.5.6).
AUTHORIZED RELEASE - Records of the authorized release of products and services for delivery to the customer including acceptance criteria and traceability to the authorizing person(s) (clause 8.6).
N/C & ACTION AUTHORITY - Records of nonconformities, the actions taken, concessions obtained and the identification of the authority deciding the action in respect of the nonconformity (clause 8.7).
QMS PERFORMANCE EVALUATION - Results of the evaluation of the performance and the effectiveness of the QMS (clause 9.1.1)
AUDIT PROGRAM RESULTS - Evidence of the implementation of the audit program and the audit results (clause 9.2.2).
MANAGEMENT REVIEW - Evidence of the results of management reviews (clause 9.3.3).
NATURE & ACTION OF N/Cs - Evidence of the nature of the nonconformities and any subsequent actions taken (clause 10.2.2).;
CORRECTIVE ACTION RESULTS - Results of any corrective action (clause 10.2.2).
Key: D&D = Design & Development | ID = Identification | N/C = Nonconformance
5 Downloadable Attachments & Illustrations
Quick reference guide to the 28 sub-clauses of the ISO 9001:2015 Standard